Prostate enlargement, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a common condition that affects many men as they age. The prostate gland, located below the bladder and surrounding the urethra, plays a crucial role in male reproductive health. However, as hormonal changes occur with age, the prostate gland may gradually grow larger, leading to various urinary and sexual symptoms. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the signs and symptoms of prostate enlargement, provide insights into identifying common warning signs, and discuss the impact of BPH on urinary and sexual function. Additionally, we will delve into available treatment options to help individuals manage this condition effectively.
Understanding Prostate Enlargement
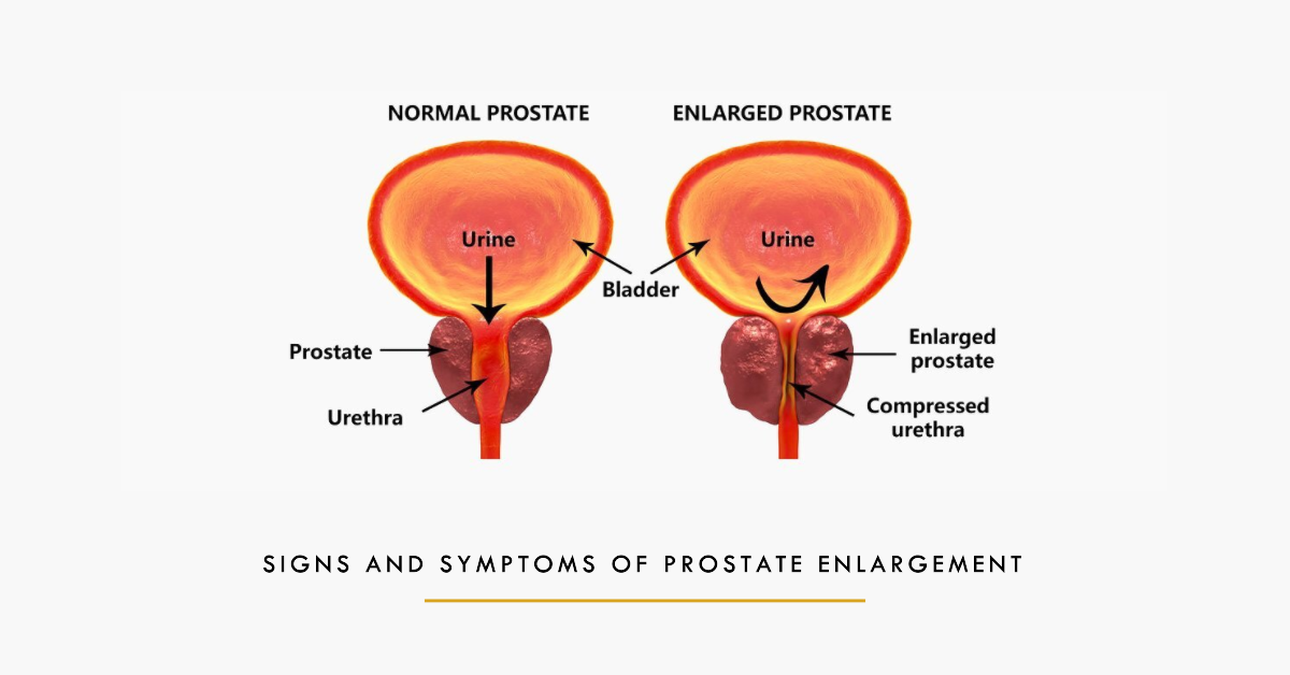
What is Prostate Enlargement?
The prostate gland is a small, walnut-shaped gland that produces seminal fluid. With age, the prostate gland can undergo hyperplasia, resulting in an enlargement known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Although BPH is not a precursor to prostate cancer, it can cause bothersome symptoms and affect urinary and sexual function.
Risk Factors for Prostate Enlargement
Several factors may increase the risk of developing prostate enlargement, including age, family history, hormonal imbalances, and certain lifestyle factors. Understanding these risk factors can help individuals assess their likelihood of experiencing BPH and monitor their prostate health accordingly.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Prostate Enlargement
Urinary Symptoms
Urinary symptoms are often the most prevalent signs of prostate enlargement. These may include:
Frequent urination: Individuals with prostate enlargement may experience the need to urinate more frequently, especially during the night.
Urgency to urinate: There may be a sudden and intense urge to urinate that is difficult to control.
Weak urine flow: Prostate enlargement can restrict the flow of urine, resulting in a weak stream that takes longer to empty the bladder.
Difficulty starting and stopping urine flow: A weakened urine stream may make it challenging to initiate urination or completely stop the flow.
Incomplete emptying of the bladder: Individuals may feel as though their bladder is not fully emptied after urination, leading to a persistent feeling of urgency.
Dribbling at the end of urination: After completing urination, some individuals may experience a dribbling sensation or leakage.
Waking up frequently at night to urinate (nocturia): Prostate enlargement can disrupt sleep patterns, causing individuals to wake up multiple times during the night to urinate.
Sexual Symptoms
Prostate enlargement can also impact sexual function. Some of the sexual symptoms associated with BPH may include:
Reduced sexual desire: Men with prostate enlargement may experience a decrease in sexual desire or libido.
Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection (erectile dysfunction): Prostate enlargement can interfere with the ability to achieve or sustain an erection, leading to difficulties in sexual performance.
Ejaculatory problems: Some individuals may experience reduced force or pain during ejaculation.
Impact on Quality of Life
The symptoms associated with prostate enlargement can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Frequent trips to the bathroom, urgency, weak urine flow, and sexual difficulties can cause frustration, embarrassment, and anxiety. Understanding the potential impact of BPH on daily life can help individuals seek appropriate treatment and support.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of prostate enlargement is crucial for seeking timely medical attention. It is important to consult a healthcare professional if you experience any of the following:
- Persistent or bothersome urinary symptoms that interfere with daily activities and quality of life.
- Sexual difficulties or changes in sexual function that are causing distress.
- Blood in the urine or semen.
- Pain or discomfort in the pelvic region.
- Worsening symptoms despite self-care measures.
Diagnosing Prostate Enlargement
Diagnosing prostate enlargement involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional. The diagnostic process may include the following:
Medical history assessment: A detailed discussion of symptoms, medical history, and family history can provide valuable insights.
Digital rectal examination (DRE): The healthcare provider examines the prostate gland by inserting a gloved finger into the rectum to assess its size, shape, and condition.
Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test: This test measures the level of a specific protein produced by the prostate. Elevated levels may indicate prostate enlargement or other prostate-related conditions.
Urine tests: These tests can help rule out urinary tract infections or other conditions that may be causing similar symptoms.
Imaging tests: In some cases, imaging tests such as ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be performed to assess the size and condition of the prostate gland.
Treatment Options for Prostate Enlargement
Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle changes can help alleviate the symptoms of prostate enlargement. These may include:
Fluid management: Avoiding excessive fluid intake before bedtime can help reduce nocturia and improve sleep quality.
Limiting caffeine and alcohol consumption: These substances can irritate the bladder, exacerbating urinary symptoms.
Maintaining a healthy weight: Obesity can contribute to prostate enlargement symptoms. Regular exercise and a balanced diet can help manage weight and reduce symptoms.
Bladder training: Techniques to gradually increase the time between urinations and relax the bladder muscles.
Medications
Medications can be prescribed to alleviate symptoms and manage prostate enlargement. Commonly prescribed medications include:
Alpha blockers: These medications relax the muscles in the prostate and bladder neck, improving urine flow.
5-alpha reductase inhibitors: These medications can help shrink the prostate gland over time, reducing symptoms.
Combination therapy: In some cases, a combination of alpha blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors may be prescribed.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
For individuals with more severe symptoms or those who do not respond to medication, minimally invasive procedures may be recommended. These procedures aim to reduce the size of the prostate or alleviate urinary obstruction. Examples include:
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP): This surgical procedure involves removing a portion of the prostate gland that is causing obstruction.
Transurethral incision of the prostate (TUIP): In this procedure, small incisions are made in the prostate to widen the urethra and improve urine flow.
Laser therapy: Different types of laser therapy can be used to remove excess prostate tissue and relieve urinary symptoms.
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of prostate enlargement is crucial for early detection and timely management. If you experience any urinary or sexual symptoms, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment. With early diagnosis and appropriate management strategies, individuals with prostate enlargement can improve their quality of life and minimize the impact of the condition. Stay proactive about your prostate health and prioritize regular check-ups to maintain optimal well-being.
FAQs about Prostate Enlargement
What causes prostate enlargement?
The exact cause of prostate enlargement is not fully understood. Age-related hormonal changes, particularly an increase in dihydrotestosterone (DHT) levels, are believed to play a significant role.
Can prostate enlargement be prevented?
While prostate enlargement cannot be completely prevented, certain lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, and avoiding excessive fluid intake before bedtime, may help reduce the risk or severity of symptoms.
Is prostate enlargement the same as prostate cancer?
No, prostate enlargement (BPH) is a non-cancerous condition, whereas prostate cancer involves the growth of cancerous cells in the prostate gland.
How often should men get screened for prostate enlargement?
The frequency of prostate enlargement screenings may vary based on individual factors and risk assessment. It is best to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate screening schedule.
Can dietary changes help manage symptoms of prostate enlargement?
While dietary changes alone may not cure prostate enlargement, they can help alleviate symptoms. Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may have a positive impact on prostate health.
Can prostate enlargement cause urinary tract infections (UTIs)?
Prostate enlargement can increase the risk of urinary tract infections. The enlarged prostate can obstruct the flow of urine, leading to incomplete bladder emptying and creating an environment favorable for bacterial growth. If you experience symptoms of a UTI, such as frequent urination, urgency, and pain or discomfort during urination, it is important to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Does prostate enlargement increase the risk of developing prostate cancer?
While prostate enlargement (BPH) is not considered a precursor to prostate cancer, the two conditions can coexist. It is possible for an individual to have both prostate enlargement and prostate cancer simultaneously. If you have concerns about prostate health or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate evaluation and screening.
Can prostate enlargement affect sexual function?
Prostate enlargement can impact sexual function in some individuals. Symptoms such as difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection (erectile dysfunction) or reduced sexual desire may occur. However, it is important to note that not all individuals with prostate enlargement experience sexual symptoms, and there are various treatment options available to address sexual concerns associated with the condition. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help determine the best course of action.
Is surgery the only treatment option for prostate enlargement?
Surgery is not always the first line of treatment for prostate enlargement. In fact, many individuals can effectively manage their symptoms through lifestyle modifications, medication, or minimally invasive procedures. Surgery is typically considered when symptoms are severe, medications are ineffective, or complications arise. It is important to have a thorough discussion with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment approach based on individual circumstances.
Can herbal supplements help with prostate enlargement?
Some herbal supplements, such as saw palmetto, have been studied for their potential benefits in managing prostate enlargement symptoms. However, the effectiveness of these supplements is still under debate, and their use should be discussed with a healthcare professional. It is important to note that herbal supplements may interact with other medications, and their safety and efficacy may vary among individuals.
Can prostate enlargement cause blood in the urine?
Prostate enlargement can sometimes lead to the presence of blood in the urine (hematuria). The enlarged prostate can cause irritation or inflammation in the urinary tract, which may result in blood appearing in the urine. If you notice blood in your urine, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for evaluation and appropriate management.
Can stress or anxiety worsen symptoms of prostate enlargement?
Stress and anxiety can exacerbate symptoms of prostate enlargement, particularly urinary symptoms such as urgency and frequency. Stress and anxiety can lead to increased muscle tension and sensitivity, which can worsen urinary symptoms. Implementing stress-management techniques, such as relaxation exercises or counseling, may help alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Are there any natural remedies or alternative therapies for managing prostate enlargement?
Some individuals may consider natural remedies or alternative therapies to manage prostate enlargement symptoms. These may include herbal supplements, acupuncture, or dietary changes. It is important to discuss these options with a healthcare professional before initiating any alternative therapies, as their efficacy and safety may vary. Additionally, it is important to ensure that any natural remedies or alternative therapies do not interfere with any prescribed medications or treatment plans.
Can lifestyle changes alone alleviate symptoms of prostate enlargement?
In many cases, lifestyle changes can help alleviate symptoms of prostate enlargement. Adopting healthy lifestyle habits such as regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding caffeine and alcohol, and practicing bladder control techniques can make a significant difference in managing symptoms. However, it is important to note that lifestyle changes alone may not be sufficient for everyone, and a healthcare professional can provide further guidance and treatment options based on individual needs.
How often should I have follow-up appointments for prostate enlargement?
The frequency of follow-up appointments for prostate enlargement may vary depending on the severity of symptoms, response to treatment, and individual circumstances. It is important to establish a follow-up plan with your healthcare professional to monitor the progression of the condition and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
Remember, if you have any concerns or questions about prostate enlargement, it is always best to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide personalized guidance based on your specific situation.